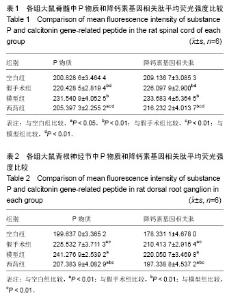
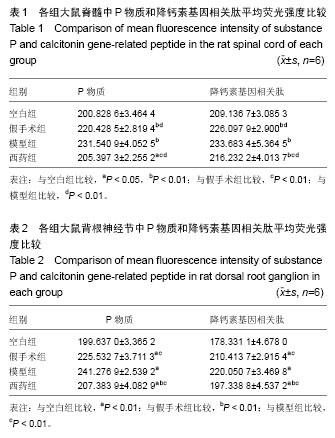
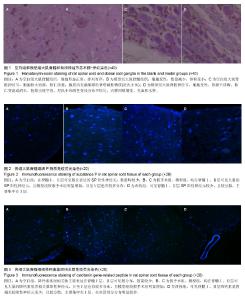
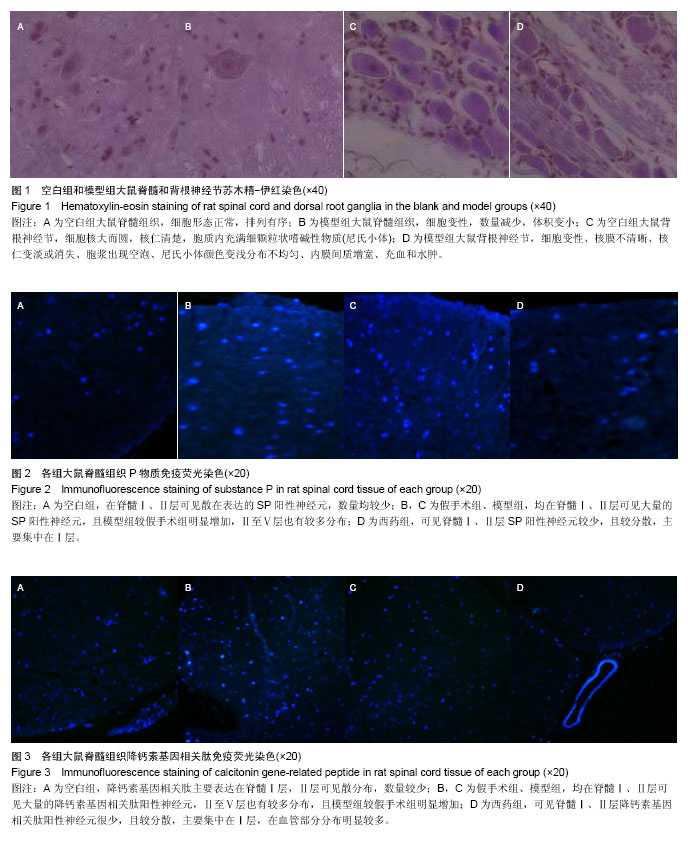
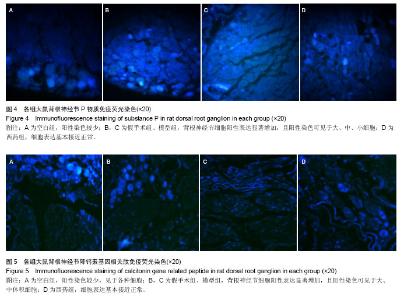
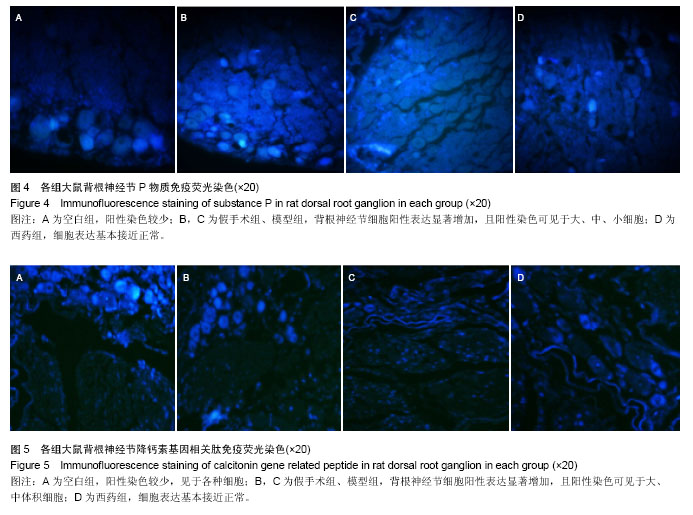
| [1] Vadalà G, Sowa GA, Kang JD.Gene therapy for disc degeneration.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2007;7(2):185-196.
[2] Evans C.Potential biologic therapies for the intervertebral disc.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:95-98.
[3] 王河忠,邵增务.椎间盘退变病因和生物学治疗研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2007,28(5):300-303.
[4] 尚琦松,刘维钢,史晨辉,等.椎间盘退行性变的影响因子及其基因和组织工程结合基因治疗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(10):1895-1899.
[5] 贺石生,侯铁胜,李明,等.自体髓核移植后大鼠腰髓背角痛觉相关物质的变化[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(9):892-894.
[6] 刘永征,徐建华,徐强,等.CT导引下精确定位神经根周围药物注射治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(2): 137-138.
[7] Wewalka M, Abdelrahimsai A, Wiesinger GF,et al.CT-guided transforaminal epidural injections with local anesthetic, steroid, and tramadol for the treatment of persistent lumbar radicular pain.Pain Physician. 2012;15(2):153-159.
[8] 黄继汉,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9): 1069-1072.
[9] 黄治平,龙毅峰.局部注射加推拿治疗腰椎间盘突出症240例[J].吉林中医药,2001,21(5):46.
[10] 韩林章,雍志军.局部注射联合手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症108例[J].人民军医,2013,56(11):1317-1318.
[11] 刘灿辉,蔡铁良,邓信林.得宝松椎管内注射治疗腰椎间盘突出症术后残留症状的效果观察[J].临床军医杂志,2012,40(1): 231-232.
[12] 胡进宇,王英伟.鞘内注射地塞米松对坐骨神经慢性压迫损伤大鼠脊髓背角降钙素基因相关肽和P物质表达的影响[J].上海医学, 2010,33(6):528-531.
[13] 姜劲挺,安文博.腰腿痛胶囊对髓核移植型腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型背根神经节中P物质和降钙素基因相关肽含量的影响[J].中医正骨,2012,24(6):18-20.
[14] 杨维琦,李世和,曾才铭.腰椎间盘突出致腰腿疼的病因探讨[J].颈腰痛杂志,2000,21(3):247-249.
[15] 张劲军,肖颖,钟觉明,等. 髓核源性坐骨神经病大鼠背根神经节磷酸化p38MAPK表达的变化[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版, 2009,30(6):652-656.
[16] 彭彩钰,赵荣光,张云燕,等. 针刺对偏头痛患者皮质扩展性抑制的影响[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(5):183-184,187.
[17] 朱遵燕,杨晓秋. 三叉神经慢性缩窄环术大鼠血降钙素基因相关肽及P物质变化[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(4):376-378.
[18] 王晋,李晨军. 原发性三叉神经痛与神经肽的相关研究进展[J].西南国防医药,2010,20(8):912-914.
[19] 焦海霞,刘庆,陈瑜,等. 电针对慢性内脏痛大鼠脊髓背角降钙素基因相关肽的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2010,26(6):594-598.
[20] 于翠萍,王琦,何明伟,等. 双氯芬酸钠对大鼠神经病理性疼痛的疗效及机制[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(10):872-875.
[21] 彭成为,余开峰,杨镭镭,等. 人神经生长因子β基因转染对神经病理性痛大鼠脊髓背角致痛物质含量的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2009,29(2):129-132.
[22] 李娟红,倪家骧.丹参注射液硬膜外腔注射对髓核移植大鼠痛阈及脊髓背角P物质和CGRP表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2008,23(8):687-690.
[23] 范隆,王国林,于泳浩.电针与丁丙诺啡合用对慢性炎性痛大鼠脊髓背角P物质、降钙素基因相关肽的影响[J].中华麻醉学杂志, 2007,27(4):368-371.
[24] 黄飞彬.右美托咪定对神经病理性疼痛大鼠痛敏和降钙素基因相关肽的影响[D]. 福州:福建医科大学,2012.
[25] 曹莹莹.CGRP在初级感觉信息调制中的作用研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2009.
[26] 于鹏,程智刚,李静怡,等.脊髓背角及背根神经节内降钙素基因相关肽与神经病理性疼痛的关系[J].实用疼痛学杂志,2007,3(6): 459-463.
[27] 李娟红,倪家骧.硬膜外腔植入髓核对大鼠脊髓背根神经节SP和CGRP表达的影响[J].颈腰痛杂志,2009,30(6):497-500.
[28] 张仲文,肖光,朱东,等.硬膜外瘢痕粘连与脊髓中P物质、c-fos的表达[J].中国现代医学杂志,2001,11(2):6-8.
[29] Kayama S, Olmarker K, Larsson K,et al.Cultured, autologous nucleus pulposus cells induce functional changes in spinal nerve roots.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(20): 2155-2158.
[30] 武俊芳,韩金珠,郭志坤,等.慢性神经痛大鼠脊髓背角P物质、降钙素基因相关肽的表达[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2008,43(4): 699-701.
[31] 张志谦,赵宝明,耿学斯.痛觉敏化的分子生物学研究进展[J].上海医学,2012,35(10):900-903.
[32] Chu H, Xia J, Yang Z,et al.Melanocortin 4 receptor induces hyperalgesia and allodynia after chronic constriction injury by activation of p38 MAPK in DRG.Int J Neurosci. 2012;122(2): 74-81.
[33] Roh DH, Yoon SY.Sigma-1 receptor antagonist, BD1047 reduces nociceptive responses and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK in mice orofacial formalin model.Biol Pharm Bull. 2014; 37(1):145-151.
[34] Hochrainer K, Racchumi G, Zhang S,et al.Monoubiquitination of nuclear RelA negatively regulates NF-κB activity independent of proteasomal degradation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012;69(12):2057-2073.
[35] 黄露露,于世英.神经病理性疼痛的中枢敏化发病机制[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2011,17(8):463-465.
[36] 蒋伟,王正国,赖西南,等.感觉神经肽P物质对成纤维细胞核因子-κB激活作用的信号机制研究[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(23): 4776-4778. |